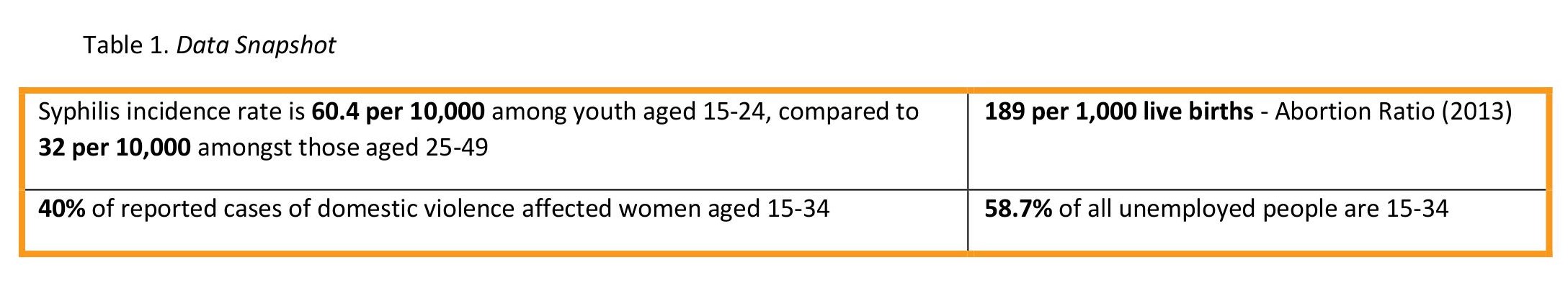
Ulaanbaatar — What is the solution to preventing sexually transmitted infections, abortion, unwanted pregnancies, domestic violence, and other issues facing Mongolia and its young people? How can we solve these to enhance young people’s employment, health, and quality of life, and to ultimately enable them to contribute meaningfully to the development of their country? The answer and solution is Life Skills Education and Comprehensive Sexuality Education for young people.
Young people are a valuable asset and bring tremendous potential to the development of Mongolia through their strengths and initiatives, their inherent sense of enthusiasm, creativity, innovation, and energy. Today’s young generations are more open, tech-savvy, connected and socially and environmentally conscious than any other generations before them. However, they are also confronted with significant challenges in their lives including a lack of opportunities for employment, and for acquiring in-demand skills for employability, high rates of STIs and gender-based violence, and other life challenges, all while managing their journey into adulthood. A solution exists to prevent and effectively respond to these challenges: Life Skills Education, and Comprehensive Sexuality Education, which help young people to acquire the knowledge, attitude, values and skills, and navigate adversities throughout their personal and professional lives.
As a key feature of the Youth Development Program, Life Skills Education seeks to empower young people with positive, responsible and self‐reliant behaviors, build their resilience in the face of rapid socio-economic change, and equip them with the skills necessary to lead productive lives that contribute to Mongolia’s development.
The revised “Life Skills Education” Facilitators’ Manuals incorporate both life skills and sexuality education elements and are the product of combined technical expertise and contributions from UNFPA, Ministry of Education, Culture, Science and Sports, Peace Corps, and the Mongolian State University of Education, and other international experts.
Over 5,000 sets of “Life Skills Education” Facilitators’ Manuals have been printed and are being distributed nationwide. User-friendly e-book versions have also been produced, as well as 1,200 student manuals including audio-book versions for youth with disabilities, to ensure inclusivity of Life Skills Education for all young people.
Through the partnership between the Government of Mongolia and UNFPA as part of YDP, Life Skills Education is being delivered through General Education Schools, TVETs, teacher-training universities, Lifelong Education Centers, Life Skills Education Halls and Youth Development Centers, reaching over 150,000 young people in 2016 alone.
The “Life Skills Education” Facilitator’s Manual Launch Event, hosted by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Science and Sports and UNFPA, promotes Life Skills Education and Comprehensive Sexuality Education for young people. It was held on Friday 10 March 2017, between 10:00am – 11:30am atSuld Hall, Best Western Premier Tuushin Hotel.
Key statistics
Youth and Life Skills Education
- The population aged 15-34 years comprises 36.2 per cent of the total; the median age is 27.5 years (2016).
- Over 5,000 sets of “Life Skills Education” Facilitators’ Manuals have been printed and are being distributed nationwide; 1,200 student manuals including audio-book versions for youth with disabilities, to ensure inclusiveness of Life Skills Education for all young people.
- Over 150,000 young people have been reached by Life Skills Education in General Education Schools, TVETs, teacher-training universities, Lifelong Education Centers, Life Skills Education Halls and Youth Development Centers in 2016.
Challenges facing young people in Mongolia
- The adolescent birth rate is high, having risen from 38 in 2010 to 40.4 births per 1,000 women aged 15-19 in 2013
- The unmet need for family planning among women aged 15-19 increased from 22.3% in 2010 to 36.4 % in 2013.
- The syphilis incidence rate increased to 60.4 per 10,000 among young people aged 15-24, compared to 32 per 10,000 among those aged 25-49.
- Over 90% of reported cases of domestic violence affected women – 40 per cent are young women aged 15-34.
- The abortion ratio rose from 169 per 1,000 live births in 2008 to 189 in 2013.
- Of unemployed people actively seeking employment, 58.7% are aged 15-34.
Reference: UNFPA 6th Country Programme (2017- 2021) Document and NSO online: http://www.1212.mn/
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
The Life Skills Education Facilitators’ Manual set is comprised of the following Life Skills Education Modules include: Introduction; 1. Self-Esteem; 2. Communication; 3. Relationships; 4. Emotional Control; 5. Decision-Making; 6. Planning; 7. Stress Management; 8. Empathy; 9. Critical Thinking; 10. GBV Prevention; 11. Substance Abuse Prevention; 12. Sexuality: STI/HIV Prevention
Links to E-Book versions of the “Life Skills Education” Facilitators’ Manuals
|
# |
Module Name |
Descriptive Sub Topics (Contents) – English |
Descriptive Sub Topics (Contents) – Mongolian |
Link |
|
|
УДИРТГАЛ / Introduction
|
General Introduction to Teaching Life Skills Education |
Амьдрах ухааны боловсролыг заах ерөнхий танилцуулга |
|
|
1 |
ӨӨРТӨӨ ИТГЭХ ИТГЭЛ/ Self-Esteem
|
Session 1. Defining & Assessing Self-Esteem Session 2.Connectedness & Self-Esteem Session 3. Uniqueness & Self-Esteem Session 4. Power & Self-Esteem Session 5. People, value and principles
|
Сэдэв 1. Өөртөө итгэх итгэлийг тодорхойлж, үнэлэх Сэдэв 2. Холбоо хамаарал ба өөртөө итгэх итгэл Сэдэв 3. Өвөрмөц байх ба өөртөө итгэх итгэл Сэдэв 4. Эрх мэдэл ба өөртөө итгэх итгэл Сэдэв 5. Хүмүүс, үнэт зүйл ба зарчим
|
|
|
2 |
ХАРИЛЦАА /Communication
|
Session 1. Types of communication Session 2. Non verbal communication Session 3. Listening skills Session 4. Assertiveness: “I statements” Session 5. Responding to persuasion Session 6. Family members communication Session 7. Work place communication
|
Сэдэв 1. Харилцаа түүний хэлбэр Сэдэв 2. Үгийн бус харилцаа Сэдэв 3. Сонсох чадвар Сэдэв 4. Өөртөө итгэлтэй харилцаа: “Би” өгүүлбэр Сэдэв 5. Ятгалгад хариу өгөх Сэдэв 6. Гэр бүлийн гишүүдийн харилцаа Сэдэв 7. Ажлын орчин дах харилцаа |
|
|
3 |
ХОЛБОО ТОГТООХ / Relationships
|
Session 1. Friendship Session 2. Date and about date rape Session 3. Establishing relationships, keeping distance Session 4. Love relationships Session 5. Decision making about having sex Session 6. Assessing and managing relationships Session 7. Ending unhealthy relationships
|
Сэдэв 1. Үерхэл нөхөрлөл Сэдэв 2. Болзоо, болзооны үеийн хүчин Сэдэв 3. Холбоо тогтоох, зай барих Сэдэв 4. Хайр дурлалын холбоо Сэдэв 5. Бэлгийн харилцаа ба шийдвэр гаргалт Сэдэв 6. Бусадтай тогтоосон харилцаандаа үнэлгээ өгөх Сэдэв 7. Эрүүл бус холбоог таслах
|
|
|
4 |
СЭТГЭЛИЙН ХӨДӨЛГӨӨНӨӨ ХЯНАХ / Emotional Control
|
Session 1. Emotions Session 2. Identifying emotions Session 3. Causes and effects of emotions Session 4. Managing emotions and behaviour Session 5. Communicating emotions |
Сэдэв 1. Сэтгэлийн хөдөлгөөн Сэдэв 2. Сэтгэлийн хөдөлгөөнийг тодорхойлох Сэдэв 3. Сэтгэлийн хөдөлгөөний шалтгаан, үр дагавар Сэдэв 4. Сэтгэлийн хөдөлгөөн, зан үйлээ хянах, зохицуулах Сэдэв 5. Сэтгэлийн хөдөлгөөнөө бусдад ойлгуулан харилцах |
|
|
5 |
БУСДЫГ МЭДЭРЧ ОЙЛГОХ / Empathy
|
Session 1. Diversity Session 2. Stereotypes Session 3. Discrimination Session 4. Disabilities Session 5. Gender and gender roles Session 6. Power and Inter-group conflict |
Сэдэв 1. Ялгаатай байдал Сэдэв 2. Тогтсон ойлголтууд Сэдэв 3. Ялгаварлан гадуурхах Сэдэв 4. Хөгжлийн бэрхшээл Сэдэв 5. Жендэр ба жендэрийн үүрэг Сэдэв 6. Эрх мэдэл ба бүлгийн зөрчил |
|
|
6 |
ШИЙДВЭР ГАРГАХ / Decision-Making
|
Session 1.. The basics of the decision making Session 2. Decision making patterns Session 3. Decision making models Session 4. Consequences of decisions Session 5. Weighing one’s options Session 6. Taking risks Session 7. Factors influencing our decisions |
Сэдэв 1. Шийдвэр гаргах тухай ерөнхий ойлголт Сэдэв 2. Шийдвэр гаргах хэлбэр Сэдэв 3. Шийдвэр гаргах загвар Сэдэв 4. Шийдвэрийн үр дагавар Сэдэв 5. Боломжийг цэгнэх Сэдэв 6. Эрсдэл хийх Сэдэв 7. Шийдвэрт нөлөөлөх хүчин зүйл |
|
|
7 |
СТРЕССИЙГ ЗОХИЦУУЛАХ / Stress Management
|
Session 1. What is stress? Session 2. Effects of stress Session 3. Types of stress Session 4. Short terms strategies of managing stress Session 5. Long term strategies of managing stress Session 6. Preventing from stress Session 7. Planning individual stress reduction
|
Сэдэв 1. Стресс гэж юу вэ Сэдэв 2. Стрессийн нөлөө Сэдэв 3. Стрессийн төрөл Сэдэв 4. Стрессийг зохицуулах богино хугацааны арга Сэдэв 5. Стрессийг зохицуулах урт хугацааны арга Сэдэв 6. Стрессээс урьдчилан сэргийлэх Сэдэв 7. Стрессийг зохицуулах хувийн төлөвлөгөө
|
|
|
8 |
ТӨЛӨВЛӨХ / Planning
|
Session 1. Identifying goals Session 2. Setting adequate goals Session 3. Making action plan Session 4. Identifying priorities Session 5. Career planning Session 6. Barriers in planning |
Сэдэв 1. Зорилгоо тодорхойлох Сэдэв 2. Сайн зорилго дэвшүүлэх Сэдэв 3. Үйл ажиллагааны төлөвлөгөө зохиох Сэдэв 4. Тэргүүлэх ач холбогдолтой зүйлээ тодорхойлох Сэдэв 5. Ажил мэргэжлийн төлөвлөгөө Сэдэв 6. Төлөвлөгөө хийхэд учрах саад бэрхшээл |
|
|
9 |
ТУНГААН БОДОХ / Critical Thinking
|
Session 1. What is critical thinking? Session 2 Information types and their differences Session 3 Writing different types of information Session 4. Analysing information Session 5. Reasoning structure Session 6. Analysing Reasoning Session 7. Credibility of sources
|
Сэдэв 1. Тунгаан бодох чадварын талаарх ерөнхий ойлголт Сэдэв 2. Мэдээллийн төрөл бүрийн ялгаатай байдал Сэдэв 3. Мэдээллийн төрлийг найруулан бичих Сэдэв 4. Мэдээлэлд дүн шинжилгээ хийх Сэдэв 5. Үндэслэлийн бүтэц Сэдэв 6. Нотолгоонд дүн шинжилгээ хийх арга Сэдэв 7. Эх сурвалжийн баталгаатай байдал |
http://www.yumpu.com/…/%D1%82%D1%83%D0%BD%D0%B3%D0%B0%D0%B0… |
|
10 |
БЭЛГИЙН АМЬДРАЛ: БЗДХ/ХДХВ –ЭЭС СЭРГИЙЛЭХ НЬ / SEXUALITY; STI/HIV PREVENTION
|
Session 1. Understanding human sexuality Session 2. Reproductive organs Session 3. Changes with puberty Session 4. Sexual orientation and gender identity Session 5. Friendship &romantic relationships Session 6. Sex and its consequences Session 7. Fertilization and pregnancy Session 8. Family planning and contraceptives methods Session 9. Unwanted pregnancy and abortion Session 10. Sexual health and Hygiene Session 11. Sexually transmitted infections and HIV/AIDS Session 12. Consequences and risks of sexually transmitted infections Session 13. Condom use
|
Сэдэв 1. Бэлгийн амьдрал Сэдэв 2. Нөхөн үржихүйн эрхтэн тогтолцоо Сэдэв 3. Шилжилтийн насны өөрчлөлт Сэдэв 4. Бэлгийн чиг баримжаа ба хүйсийн баримжаа илэрхийлэл Сэдэв 5. Үерхэл нөхөрлөл, хайр дурлалын харилцаа Сэдэв 6. Бэлгийн харилцаа түүний үр дагавар Сэдэв 7. Үр тогтолт ба жирэмслэлт Сэдэв 8. Гэр бүл төлөвлөлт ба жирэмслэхээс сэргийлэх арга хэрэгсэл Сэдэв 9. Хүсээгүй жирэмслэлт ба үр хөндөлт Сэдэв 10. Бэлгийн эрүүл мэнд ба эрүүл ахуй Сэдэв 11. Бэлгийн замаар дамжих халдвар ба ХДХВ/ ДОХ Сэдэв 12. Бэлгийн замаар дамжих халдварын үр дагавар ба эрсдэл Сэдэв 13. Бэлгэвчийн хэрэглээ
|


